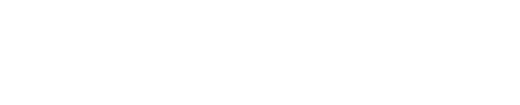
What is diversity?
Diversity refers to the mix of people in an organisation – that is, all the differences between people in how they identify in relation to their:
- SOCIAL IDENTITY e.g., Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander background, age, gender, caring responsibilities, LGBTIQ+ status, culture or faith.
- PROFESSIONAL IDENTITY e.g., profession, education, organisational level, location.
These aspects come together in a unique way for each individual and shape the way they view and perceive their world and workplace.
DCA’s diversity definition is IDENTITY-BASED, as it recognises that the starting point should be how each of us identifies ourselves rather just how others categorise or label us.
This diversity definition also takes into account multiple INTERSECTING diversity dimensions. A person’s identity is often influenced by multiple dimensions. For each individual, these different dimensions come together or ‘intersect’ to form their particular identity.
For example, an individual may not just identify as a woman, but also someone with a trans history who comes from a culturally diverse background.
Want to use our definition?
Where you wish to refer to our diversity definition publicly, it must be correctly attributed to DCA.
- Formal attribution to DCA is required where references to this definition are in a written format.
- Citing DCA as a source will suffice where the reference is made in a verbal format.
The suggested citation for this definition is:
Diversity Council Australia, Diversity Definition, Sydney, DCA, 2025
What is inclusion?
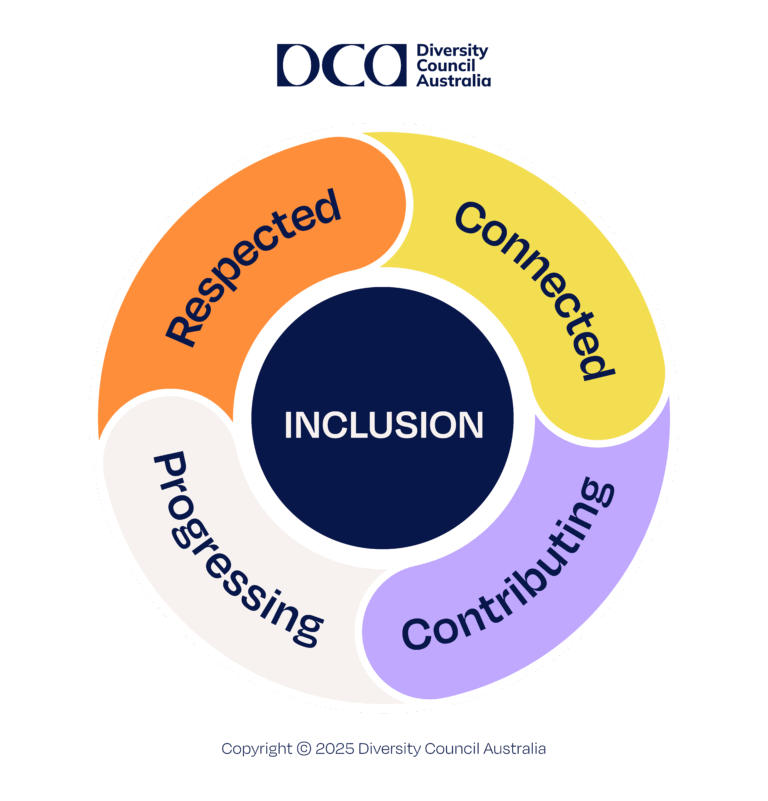
Inclusion refers to getting the mix of people in an organisation to work together to improve performance and wellbeing.
Inclusion in a workplace is achieved when a diversity of people (e.g. ages, cultural backgrounds, genders, perspectives) feel that they are:
- RESPECTED for who they are and able to be themselves;
- CONNECTED to their colleagues and feel they belong;
- CONTRIBUTING their perspectives and talents to the workplace; and
- PROGRESSING in their career at work (i.e. have equal access to opportunities and resources)
Want to Use Our Model?
Where you wish to refer to our inclusion model publicly, it must be correctly attributed to DCA.
- Formal attribution to DCA is required where references to this definition are in a written format.
- Citing DCA as a source will suffice where the reference is made in a verbal format.
The suggested citation for this definition is:
Diversity Council Australia, Inclusion Model, Sydney, DCA, 2025.
Log in for examples of how other organisations have defined diversity and inclusion in their policies.
Member-only content
Gain full access with DCA membership!
If your organisation has just signed up, your access will be activated as soon as payment is received.